
What is trx-control?
trx-control is a modern extensible software system for Linux to control amateur radio transceivers and to receive automatic status updates from them in real-time.
Besides transceivers, it is also used to control a variety of other equipment, from GPS receivers to GPIO pins.
It is user extensible and integrates well with third-party software or online systems with extensions written in the easy to learn Lua programming language.
trx-control is modular by design, makes optimal use of your computers hardware and was created with you, the user, in mind.
Documentation
Project Goals
-
Create an open and easily extensible system to control mainly transceivers, but also other hardware, and integrate with third-party software.
-
Make it easy to add support for new transceivers or other devices.
-
Provide an easy to implement and easy to use client/server protocol based on the exchange of JSON-formatted data over the network.
-
Use a multi-language approach where the core of the system is written in C whereas extensions and drivers can be written in the easy to learn Lua programming language, lowering the entry barrier a lot.
-
No programming skills are needed to add new transceivers if they use one of the already supported CAT protocols.
-
Use a multithreaded, asynchronous approach at the core of the software.
| trx-control is under active development. Things may change in incompatible ways. I try, however, to keep the documentation and this website up to date. If you find inconsistencies, errors or bugs, please file a PR on the Github page (see Source Code). |
System Overview
At the core of a trx-control installation is trxd(8), the daemon that handles clients (IPv4 and IPv6) and controls the devices and extensions by exchanging JSON-formatted data with the clients and talking to the transceivers and other devices over whatever interface they use. All communication between the clients and trxd(8) is either done using NDJSON packages over a plain TCP/IP socket or JSON packages over a WebSocket.
Multiple clients can simultaneously connect to trxd(8), controlling an unlimited number of transceivers, GPIO pins and extensions:
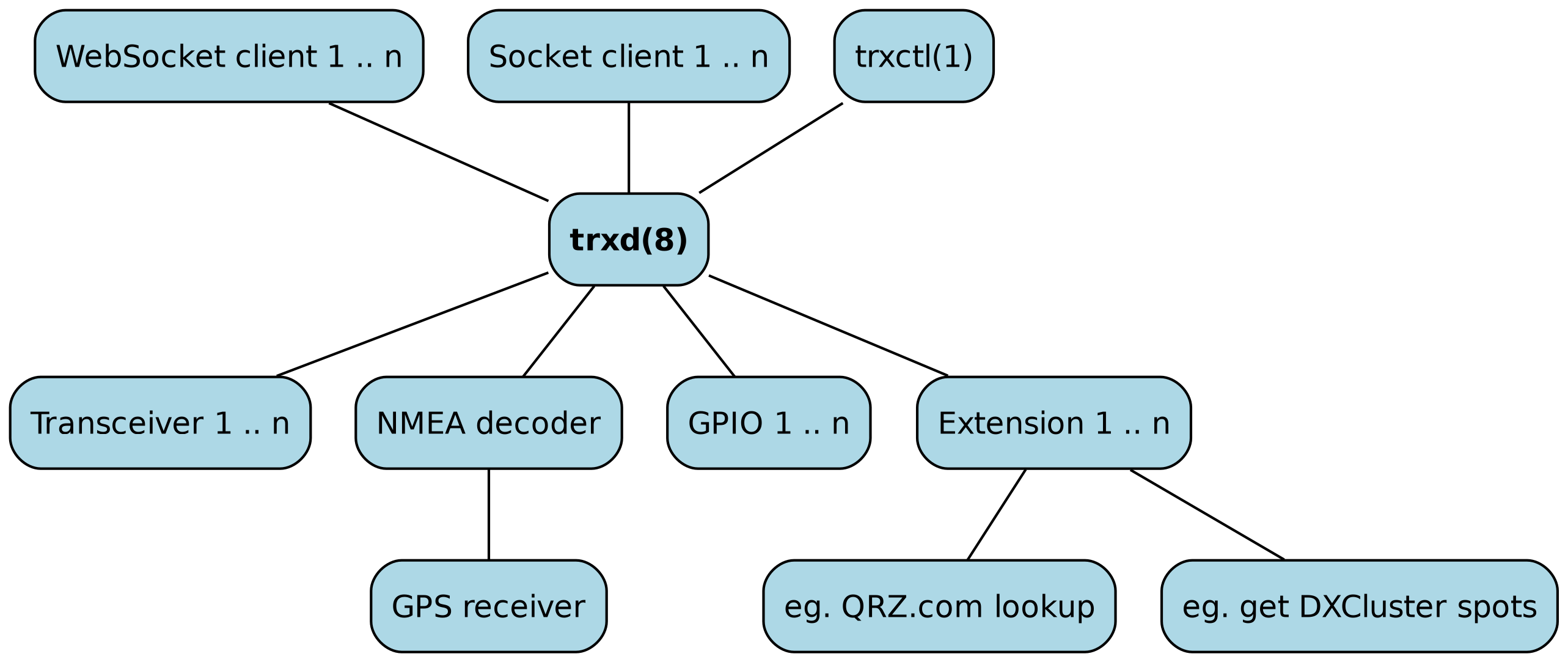
trxd(8) supports transceivers that can automatically send status updates (e.g. Yaesu FT-710 etc.) as well as transceivers that require polling (e.g. older Yaesu FT-897 etc.)
Devices and Extensions
Transceivers
trx-control supports the following transceivers, more will be added over time:
| Brand | Model(s) |
|---|---|
Connect Systems Inc. |
CS7000-M17, CS70000-M17 GPS, CS7000-M17 PLUS |
ICOM |
IC-705 |
JVC Kenwood |
TH-D75E, TH-D75A |
Yaesu |
FT-710, FT-817, FT-857, FT-891, FT-897, FT-991a, FTX-1 |
A special simulator transceiver driver exists for development and testing purposes.
GPIO
| Brand | Model(s) |
|---|---|
bmcm |
USB-PIO / OR8 (attached to USB-PIO) |
GPS/NMEA
Any GPS/Glonass/BeiDou etc. receiver that emits fix data as NMEA sentences.
Extensions
| Name | Purpose / Comments |
|---|---|
config |
Access the trxd(8) configuration (read only) |
dxcluster |
Get DX (or SOTA) cluster spots in real time or query the last n spots |
hamqth |
Lookup callsigns the HamQTH.com database |
logbook |
A simple logbook for QSOs using a PostgreSQL database |
memory |
Manage memories and memory groups |
ping |
Check if the trxd(8) service is alive |
qrz |
Lookup callsigns in the QRZ.com database (requires a QRZ.com subscription for full functionality) |
tasmota |
Control power plugs with the Tasmota alternative firmware |
Client Apps
The trx-control protocol is open for anyone do develop a client or integrate trx-control into their own software. Nevertheless we do provide a client app aimed at mobile devices.
The trx-control client app is available in the Google Play Store as well as in the Apple App Store.

(Google Play and the Google Play Logo are trademarks of Google LLC.)
Social Media
Bluesky
Follow HB9SSB on Bluesky: @hb9ssb.bsky.social
Matrix Room
There is a Matrix chat room #trx-control:matrix.org to discuss trx-control: #trx-control:matrix.org
FAQ
Can I run trx-control on Windows?
While trx-control requires a Linux system to run on, it can as well be used on Windows. Install the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) and install the prebuilt binary packages for the Linux distribution you did choose and install in WSL.
Another option might be to use a desktop virtualizer like VirtualBox or VMWare Workstation (both are free) or running it in a container, e.g. using Docker Desktop.
How can I access USB devices from within WSL?
You can connect a USB device to a Linux distribution running on WSL 2 using the USB/IP open-source project, usbipd-win. See the following articles for details:
Can I run trx-control in a container?
Yes, just make sure to properly setup networking and access to USB devices. Also, if service advertising using mDNS is to be used to announce the Websocket service, then the network within in the container has to be correctly configured so that mDNS packages are passed (port 5353/udp).
Talks and Information Material
From Supporting Elephants to Controlling Shortwave Transceivers: 15 Years of Lua. A recording of a talk during the "Celebrating 30-years of Lua" special edition Lua Workshop 2023 in Rio de Janeiro:
Presentation slides from the "Software Defined Radio & Amateur Radio" devroom that I co-organised at FOSDEM 2024 in Brussels:
Presentation slides from the Dreiländereck-Sysop-Treffen 2024:
Video and slides from a trx-control presentation I gave in may at HB9AG, my local club:
Flyers and cards:
| Print the flyers on A4 paper in landscape mode and fold them twice from the outside inwards so that the title is on top and the page with the address is on the back. |
Prebuilt Binary Packages
Prebuilt binary packages for various Linux distributions and machine architectures can be downloaded from https://trx-control.msys.ch/pub/repos
Source Code
trx-control is open source software licensed under the MIT license. You can access the source code on GitHub at https://github.com/hb9ssb/trx-control